Understanding how to calculate welding strength is crucial for ensuring welds are strong, safe, and able to handle the expected load. When I first got into welding, I didn’t realize how much science was behind a good weld.
It’s not just about making the weld look nice—it needs to hold up under pressure. If a weld fails, it can lead to serious structural issues or even safety hazards.
Photos by pdfcoffee
Through experience, I’ve learned how to calculate welding strength in different scenarios, whether it’s for a simple fabrication job or a high-stress structural weld.
If you’re trying to figure out how much weight or force a weld can handle, you’re in the right place. I’ll break everything down in an easy-to-understand way so you can confidently assess your welds.
Why Welding Strength Matters
The strength of a weld determines whether it will hold up under stress or fail. Whether you’re working on structural steel, pipelines, automotive frames, or industrial machinery, knowing the weld’s strength helps you ensure safety, durability, and efficiency.
Some key reasons why welding strength calculations are important:
- Prevents weld failures – Weak welds can crack or break under pressure.
- Ensures structural integrity – Buildings, bridges, and equipment depend on strong welds.
- Meets industry standards – Many industries have strict welding strength requirements.
- Improves weld efficiency – Using the right amount of weld material reduces waste.
Factors That Affect Welding Strength
Several factors impact the strength of a weld, and each one plays a role in how much force the weld can handle.
- Weld Type – Fillet welds, butt welds, groove welds, and lap welds all have different strength characteristics.
- Material Type – Mild steel, stainless steel, aluminum, and other metals have different tensile strengths.
- Weld Size – The thickness and length of the weld determine its load-bearing capacity.
- Penetration – A deeper, fully fused weld is stronger than a shallow weld.
- Welding Process – MIG, TIG, stick, and flux-core welding all produce different weld strengths.
- Load Type – The direction of force (tension, compression, shear, bending) affects how a weld performs.
How to Calculate Welding Strength
There are different methods to calculate welding strength, but the most common approach involves determining the load-bearing capacity of the weld based on its type and size.
Weld Strength Formula
For most welding applications, we use the formula:
Welding Strength=Weld Size×Length×Shear Strength
Each term in this equation plays a key role:
- Weld Size – The throat thickness of the weld (for fillet welds) or the width of the fused joint (for groove welds).
- Length – The total length of the weld in inches.
- Shear Strength – The material’s resistance to shearing force, usually measured in PSI (pounds per square inch).
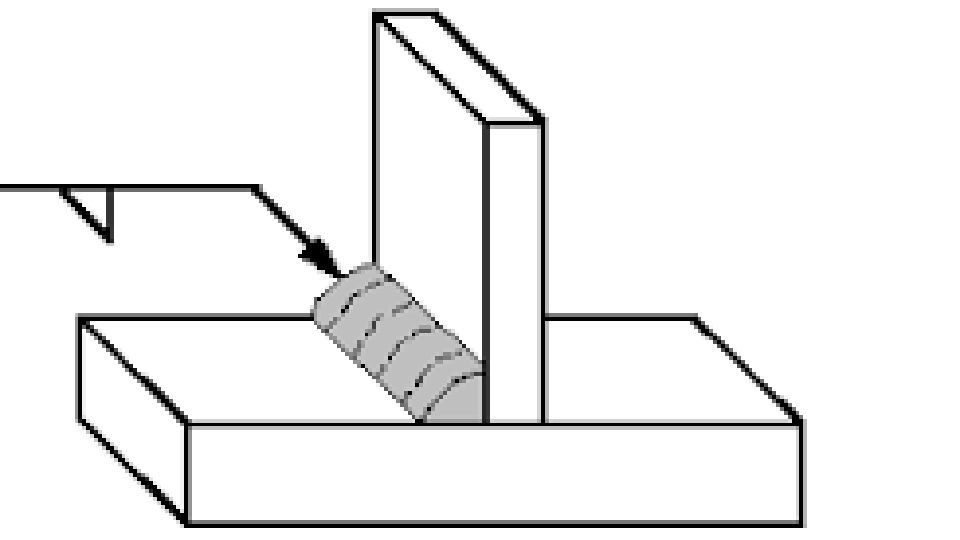
Calculating Strength of Fillet Welds
Fillet welds are one of the most common types of welds used in steel structures and fabrication. Their strength depends on the throat size (T) and the length of the weld.
To calculate the throat size, use this formula:
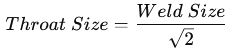
Then, apply the strength formula:
Welding Strength=Throat Size×Length×Shear Strength
Example Calculation for a Fillet Weld
Let’s say we have:
- A 1/4-inch fillet weld
- A 6-inch long weld
- A shear strength of 60,000 PSI
First, calculate the throat size:
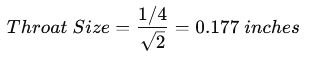
Then, calculate the weld strength:
0.177×6×60,000=63,720 pounds
So this weld can handle 63,720 pounds of shear force.
Calculating Strength of Butt Welds
Butt welds are stronger than fillet welds because they provide full penetration and a continuous joint. The strength of a butt weld is calculated using:
Welding Strength=Weld Area×Tensile Strength
The weld area is found by multiplying the thickness of the material by the weld width.
Example Calculation for a Butt Weld
Let’s say we are welding 1/2-inch thick steel plates with a full penetration butt weld and the material has a tensile strength of 70,000 PSI.
Weld Area=0.5×1=0.5 square inches
Welding Strength=0.5×70,000=35,000 pounds
This weld can handle 35,000 pounds of tensile force.
How to Ensure Maximum Weld Strength
Even if calculations show a weld is strong enough, it’s always best to optimize the weld for maximum strength. Here are a few tips:
- Use Proper Welding Techniques – Poor technique can weaken even a well-calculated weld.
- Ensure Full Penetration – Deep penetration results in stronger welds.
- Match the Filler Metal to the Base Metal – Use the correct welding wire or rod.
- Avoid Undercutting or Porosity – These defects can weaken the weld.
- Inspect the Welds – Use visual inspection, dye penetrant tests, or X-rays for critical welds.
Mistakes When Calculating Weld Strength
I’ve seen many welders make simple but costly mistakes when estimating weld strength. Here are a few things to watch out for:
- Not accounting for load direction – Shear and tensile loads affect welds differently.
- Using incorrect shear or tensile strength values – Always check material specifications.
- Overlooking weld defects – A theoretical calculation means nothing if the weld has porosity or cracks.
- Ignoring welding codes and standards – Certain projects require welds to meet specific regulations.
Conclusion
Calculating welding strength isn’t just a technical exercise—it’s a crucial step in making sure your welds are safe, reliable, and built to last.
If you’re welding mild steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, the right calculations help prevent failures and improve weld quality.
For most jobs, fillet weld strength depends on throat thickness, length, and shear strength, while butt welds depend on weld area and tensile strength. Always double-check your numbers and inspect the welds carefully to ensure maximum durability.
If you’re just starting out, don’t worry—it gets easier with practice. The more you work with different materials and loads, the better you’ll understand how to determine the perfect welding strength for any job.
FAQs
How do you calculate the strength of a weld?
Multiply the weld’s throat size, length, and shear strength for fillet welds. For butt welds, use the weld area and tensile strength.
Which weld is stronger: fillet weld or butt weld?
Butt welds are generally stronger because they provide full penetration, while fillet welds rely on shear strength.
Does welding rod selection affect weld strength?
Yes, using the wrong filler metal can weaken the weld. Always match the filler metal to the base metal.
What happens if a weld is too weak?
A weak weld can crack, break, or fail under load, leading to potential structural issues or safety hazards.
How can I improve weld strength?
Use proper technique, ensure full penetration, match the filler metal correctly, and inspect welds for defects.




